Passive Optical Network
Unlock New Possibilities with Reliable Broadband Service
- Home
- Technologies
- Passive Optical Network
As fixed broadband service is gradually becoming a necessity across the world, Passive Optical Network (PON) has emerged as the driving technology for this expansion. In addition to enabling home and business connectivity, it is the technology of choice in various government initiatives to bridge the digital divide due to its bandwidth capacity, reliability, energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
GPON (Gigabit-Capable Passive Optical Network) is an ITU standard (ITU G.984) that can support up to 2.5 Gbps shared bandwidth on downstream traffic and 1 Gbps on upstream traffic. It is being employed to build national broadband networks in several countries. The advantage of PON architecture is that a single Optical Line Terminal (OLT) port installed at a hub location can typically deliver broadband services to up to 128 end-points or Optical Networking Terminals (ONT) within a 20 km using simple passive optical splitters in the field. Higher-speed PON technology variants have also emerged based on new technology standards. XGS-PON is an ITU standard that enables up to 10 Gbps symmetrical bandwidth for subscribers. NG-PON2 (TWDM PON) is another ITU standard that supports multiplexing of multiple wavelengths with tunable optics to enhance capacity and deliver faster service restoration in case of enterprise applications.

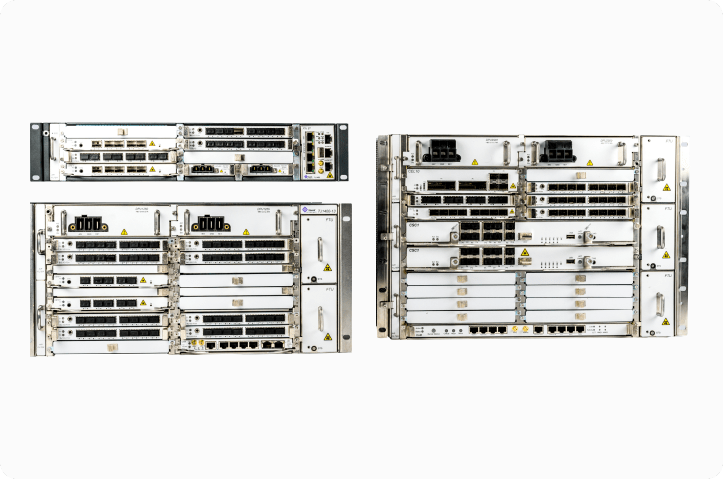
Tejas has comprehensive ONT and OLT platform solutions which have been used successfully in various deployment scenarios, including public infrastructure, campus network, smart cities and rural broadband.
Tejas Offerings – Key Highlights

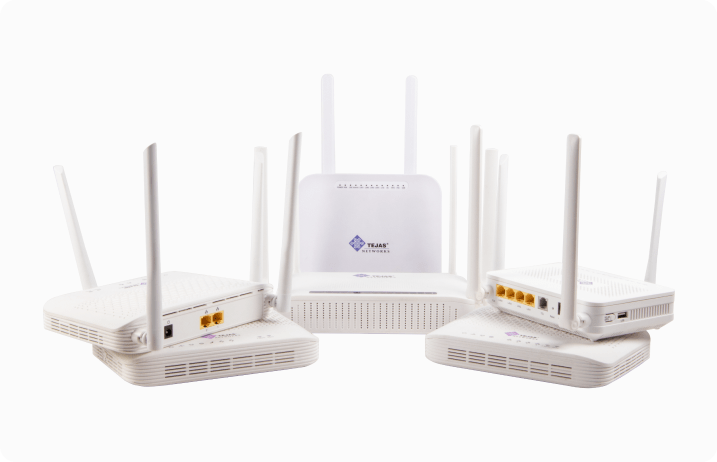
Wide Range of Residential, Enterprise and Industrial ONTs
Proven Interoperability with Third Party Systems

Support GPON, XGS-PON and Combo PON

Dense OLT Realization for TCO Optimization
Converged Platforms Supporting Multi-technologies




